Belonging to the class of medications called selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs). It works by increasing the amounts of serotonin and norepinephrine, natural substances in the brain that help maintain mental balance and stop the movement of pain signals in the brain. div {text-align: center;}
Click here
TAKE CYMBALTA.Brand Name
CYMBALTA
Generic Name
duloxetine
Drug Class
Antidepressants,SNRIs
Prototype
Venlafaxine
Pregnancy Category
C
Here's what it looks like
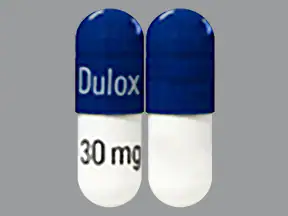
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Major Depressive Disorder
Initial Treatment :Administered at a total dose of 40 mg/day (given as 20 mg BID) to 60 mg/day (given either once a day or as 30 mg BID) without regard to meals. Maintenance/Continuation/Extended Treatment: Patients should be periodically reassessed to determine the need for maintenance treatment and the appropriate dose for such treatment
Generalized Anxiety Disorder
Initial Treatment: start dose for Cymbalta is 60 mg administered once daily without regard to meals. For some patients, it may be desirable to start at 30 mg once daily for 1 week, to allow patients to adjust to the medication before increasing to 60 mg once daily.
Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathic Pain
Cymbalta should be administered at a total dose of 60 mg/day given once a day, without regard to meals.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
In patients receiving a serotonin reuptake inhibitor in combination with a monoamine oxidase inhibitor, there have been reports of 10 serious, sometimes fatal, reactions including hyperthermia, rigidity, myoclonus, autonomic instability with possible rapid fluctuations of vital signs, and mental status changes that include extreme agitation progressing to delirium and coma
SIDE EFFECTS
| Common Side Effects | Serious Side Effects |
|---|---|
| drowsiness | lightheadedness |
| nausea | increased energy |
| constipation | difficult urination |
| loss of appetite | impotence |
| dry mouth | jaundice |
| increased sweating | pounding heartbeats |
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Inhibitors of CYP1A2
1.co-administered with fluvoxamine (a potent CYP1A2 inhibitor)
Other drugs that inhibit CYP1A2
1.cimetidien
2.ciproflosacin
3.enoxacin
Pharmacokinetics
Peak: 6 h. Metabolism: Metabolized in the liver by CYP2D6 and CYP1A2. Elimination: 70% excreted in urine, 20% excreted in feces. Half-Life: 12 h (8–17 h).
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
Assessment & Drug Effects
1.Ensure that a complete list of all concurrent medications is obtained.
2.Monitor for S&S of numerous drug-drug interactions
3.Lab test: LFTs for unexplained abdominal pain or enlarged liver
4.Monitor closely for and report suicide ideation, especially when drug is initiated or dosage changed
5.Report emergence of any of the following: anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, psychomotor restlessness, hypomania, and mania
6.Monitor BP, especially in those being treated for hypertension.
Patient & Family Education
1.The beneficial effects of this drug may not be felt for approximately 4 wk.
2.Report any of the following: suicidal ideation (especially early in treatment or when dosage is changed), palpitations, anxiety, hyperactivity, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, restlessness.
3.Do not abruptly discontinue taking this drug. Notify physician if side effects are bothersome.
4.Avoid or minimize use of alcohol while taking this drug.
5.Report emergence of any of the following: anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, psychomotor restlessness, hypomania, and mania
6.Do not self-treat for coughs, colds, or allergies. Consult physician.
7.Do not breast feed while taking this drug.
Click here for MORE INFORMATION!